Phytoplankton Dynamics and Its Further Implication for Particulate Organic Carbon in Surface Waters of a Tropical/Subtropical Estuary
Phytoplankton succession along with salinity in estuaries not only influences the riverine ecosystem but also interferes our understanding of riverine materials (e.g., organic carbon) transport to the sea. Four cruises were conducted in a mid-size river and its estuary (i.e., the Wanquan River) to elucidate the riverine phytoplankton decease along increasing salinity and to quantify the amount of algal particulate organic carbon (POC) present in the system at different seasons. CHEMTAX calculations suggested that chlorophytes were the main chlorophyll a (CHLa) contributor in the dissolved inorganic phosphorus-limited river, which contributed over 60 % of the total CHLa. Microscopy further revealed that the dominant species was Scenedesmus sp. In the estuary, phytoplankton succession along with salinity in the estuary
was observed. Chlorophyte contribution to total CHLa dramatically decreased from over 60 % in the river (S=0) segment to <2 % in the estuary (i.e., 0<S<30), whereas simultaneously, diatoms increased from <3 % to over 80 %. Microscopy revealed that Scenedesmus sp. was dramatically removed with increasing salinity, and the cell density decreased from over 540×103 cell/L (S=0) to almost 0 when S>20, suggesting the removal of riverine algae in the estuary. The mean algal POC concentration ranged from 80 μg/L (summer) to 140 μg/L (winter), and the riverine algal POC accounted for 6–56 % of the bulk riverine POC. The annual flux of riverine algal POC was estimated to be 660 tons.
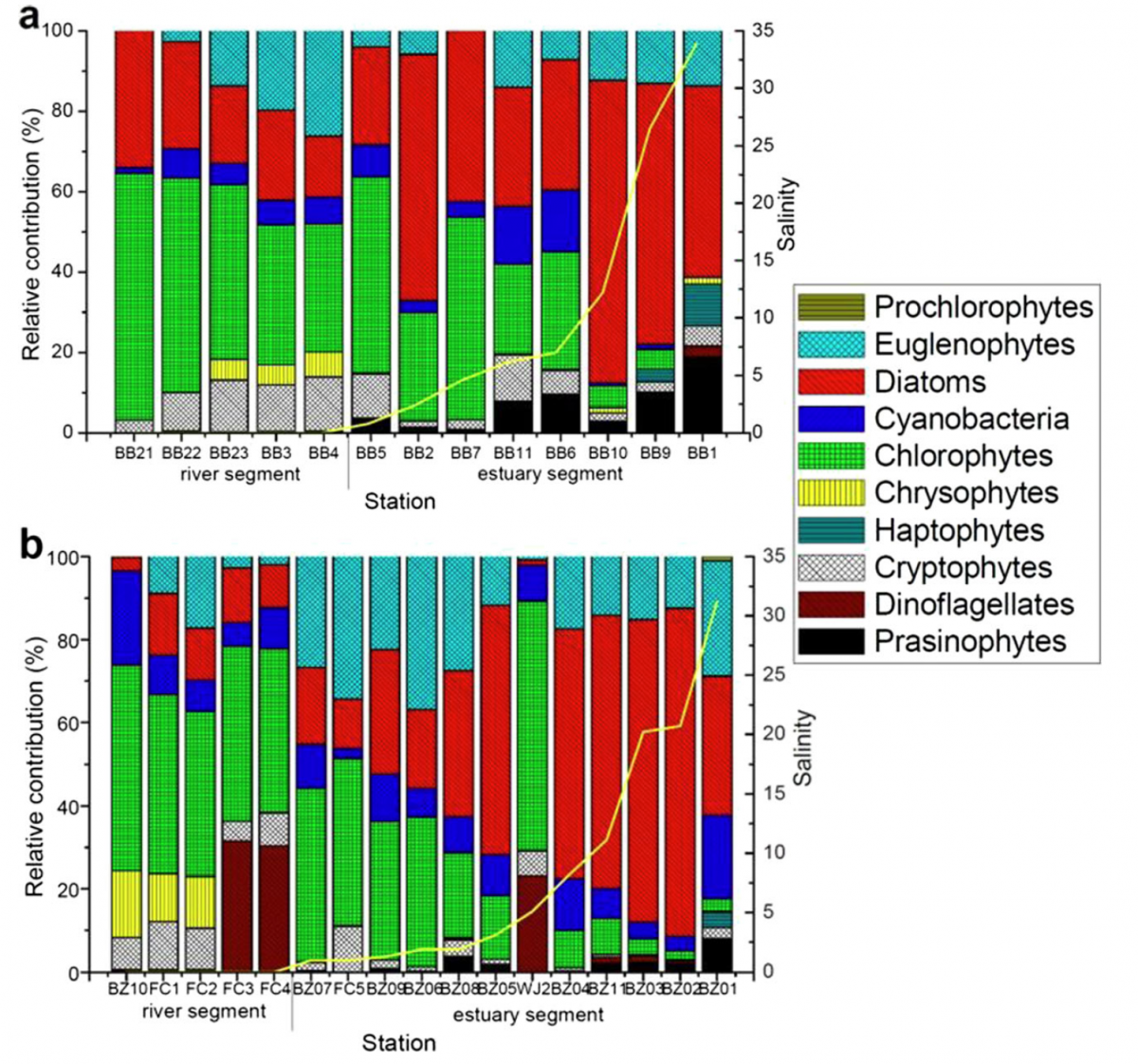
Fig.1 Phytoplankton contribution to total CHLa as estimated by CHEMTAX (a 2007, b 2008; for 2007, total CHLa=CHLa; for 2008, total CHLa=CHLa+DVCHLa; yellow line indicates the salinity)
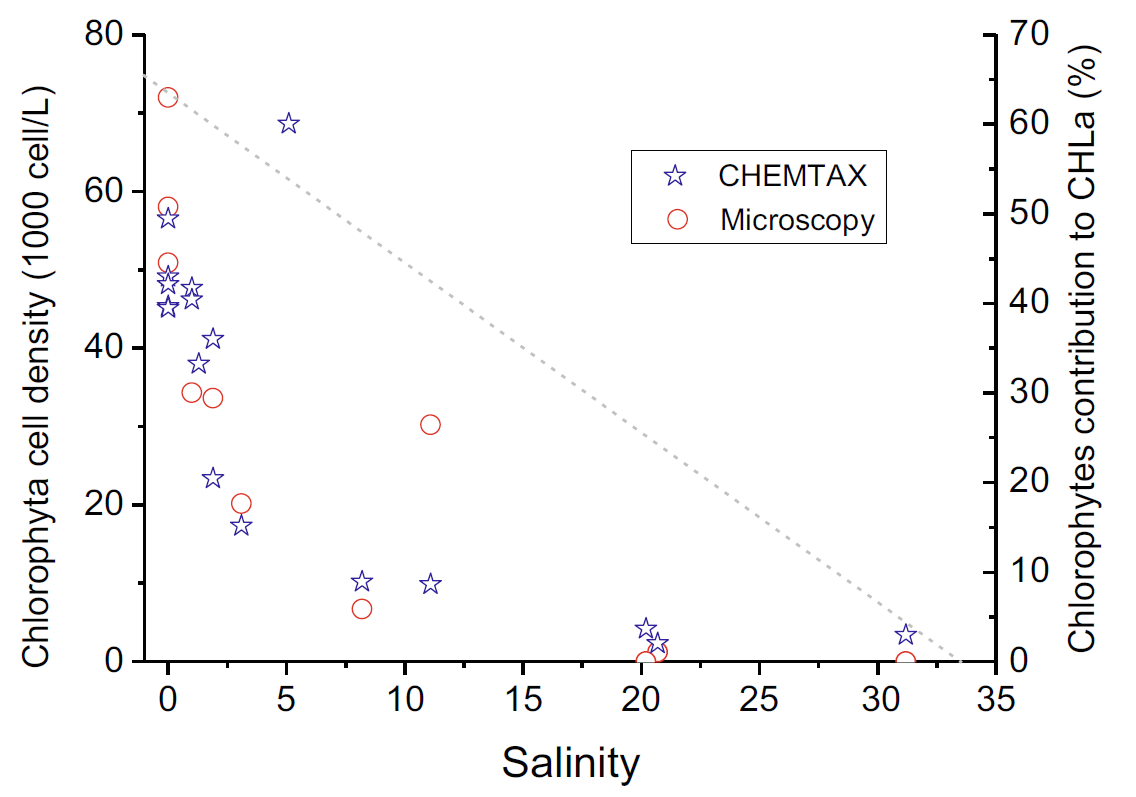
Fig.2 Chlorophytes extinction along with salinity in summer of 2008
(dashed line indicates the conservative dilution)
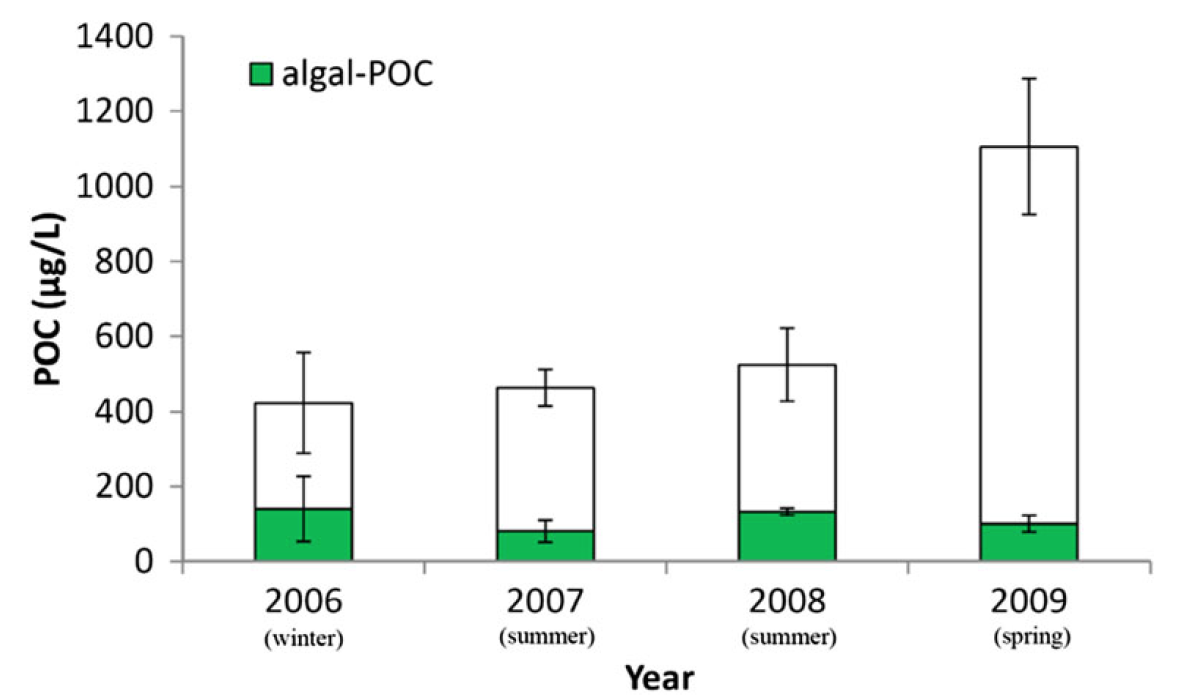
Fig.3 Algal POC compared to bulk riverine POC (i.e., S=0) for theWQ
River (POC data derived from Wu et al. 2013)
List of relate results:
-
Estuaries and Coasts ,
2015 ,
28(3)
: 905-916.
